MegaDemo sample (.NET)
Concepts Covered
This is the combined sample demonstrating various features of Remoting SDK, supported by Remoting SDK for .NET:
- TCP and HTTP channels
- Different message types
- URL schemes
- Simple values and structures transfer
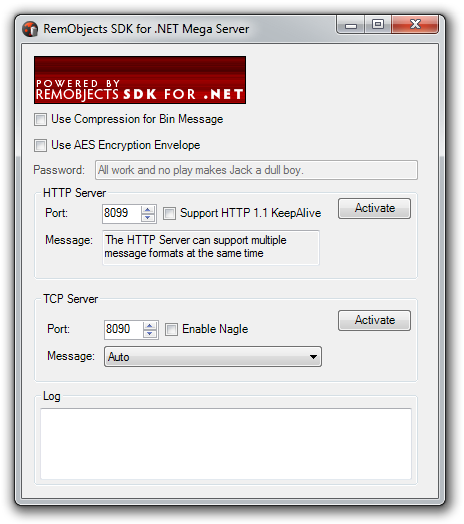
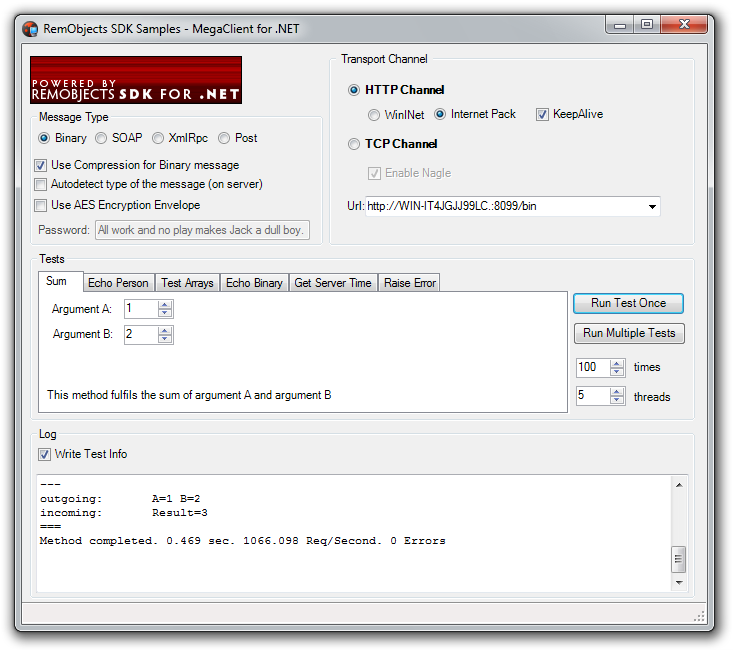
Implementations Across Platforms
The MegaDemo Client can be used together with the MegaDemo Server for .NET or the MegaDemo Server for Delphi. The MegaDemo Server can be used by the clients on various platforms as well:
- MegaDemo Client for .NET
- MegaDemo Client for Delphi
- MegaDemo Client for Cocoa
- MegaDemo Client for Java or Android
- MegaDemo Client for JavaScript The Cocoa edition takes advantage of ROZeroConf, so make sure Bonjour for Windows is running on the server computer.
Getting Started
Build and launch the MegaDemo sample server for the platform you like. Activate HTTP, TCP or both servers in the server application. The MegaDemo client allows you to test the HTTP or TCP client channels class together with Binary, SOAP, XmlRpc or Post message classes. Data compression can be enabled or disabled for Binary messaging. The AES Encryption Envelope can be enabled or disabled for all types of messages.
Set the Transport Channel:
HTTP Channel: Set the target URL, set the type of the client channel WinINET or Internet Pack.TCP Channel: Set the target URL and theEnable Nagleparameter to enable Nagle's algoritm on wikipedia.org.
Set the Message:
Check the URL:
- Watch how the value in the
Urlfield changes to follow your channel and message selection - Adjust the host name and port number in the
Urlfield if necessary - Try to input a custo, Target Url into that field, see the channel and message selection radio buttons changing accordingly
Try to perform various operations with the server. Select a desired tab page, enter required data into the fields and click the Run Test Once button. You can view the operations log in the drawer log window, click the Write Test Info checkbox to enable or disable logging. The operations that can be performed on the server are:
Sum: Sums two integer values.EchoPerson: Sends a structure (Person type) to the server and back.Test Arrays: Sends an array of different element type (including array of structures) to the server and back.Echo Binary: Sends a binary stream to the server and back.Get Server Time: Calls a parameterless remote function (get server time).Raise Error: Handles an exception raised on the server, including exceptions of custom type.
Set the number of threads and the number of service calls and click Run Multiple Tests. The corresponding number of threads will be created on the client side. Each thread will call the service operation for the defined number of times.
Examine the code
The server side represents a RemObjects SDK server that allows to use either the HTTP or the TCP protocol or both together.
HTTP server channel activation in the Main.cs file:
private void bActivateHttp_Click(Object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Boolean lNewState = !ipHttpServerChannel.Active;
if (lNewState)
{
ipHttpServerChannel.Port = Convert.ToInt32(nudPortHttp.Value);
ipHttpServerChannel.KeepAlive = chkKeepAlive.Checked;
bActivateHttp.Text = "Deactivate";
AddToLog("Http Server Channel has been activated.");
}
else
{
bActivateHttp.Text = "Activate";
AddToLog("Http Server Channel has been deactivated.");
}
ipHttpServerChannel.Active = lNewState;
pnlHttpConfig.Enabled = !lNewState;
}
The client side contains the abstract class BaseThreadState that allows to execute service operations and log the result information.
Main.cs:
private abstract class BaseThreadState
{
...
protected IMegaDemoService Service = null;
public virtual void ThreadProc()
{
IMessage lMessage = this.Message.Clone();
IClientChannel lClientChannel = CloneClientChannel(this.ClientChannel);
Boolean lIsRunOnce = this.Count == 1;
this.Service = CoMegaDemoService.Create(lMessage, lClientChannel);
String lLog = "";
double lStart, lEnd;
for (Int32 i = 1; i <= this.Count; i++)
{
try
{
lStart = Environment.TickCount;
DoTest();
lEnd = Environment.TickCount;
this.ExecutionTime += ((lEnd - lStart) / 1000);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
lLog += "Exception: " + ex.Message + Environment.NewLine;
this.ErrorCount++;
}
}
Boolean lIsLastThread = false;
if (Interlocked.Decrement(ref AsyncOpsCount) == 0)
{
AsyncOpsAreDone.Set();
lIsLastThread = true;
...
}
}
public abstract void DoTest();
public abstract String LogMethod();
Each type of operations (Sum, EchoPerson, etc) represents each own class - descendant of BaseThreadState
Main.cs file. Sum class impementation
private class SumMethodThreadState : BaseThreadState
{
public Int32 A;
public Int32 B;
public Int32 Result;
public override void DoTest()
{
this.Result = Service.Sum(this.A, this.B);
}
public override String LogMethod()
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine("Sum");
sb.AppendLine("---");
sb.AppendLine(String.Format("outgoing:\tA={0} B={1}", this.A, this.B));
sb.AppendLine(String.Format("incoming:\tResult={0}", this.Result));
sb.AppendLine("===");
return sb.ToString();
}
}
When you click Run Test Once or Run Multiply Tests, the client chooses the method to execute and calls it for the corresponding number of times:
private void bRunMultipleTimes_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SetAccess(false);
String lMethodName = "";
switch (tabCtrlTests.SelectedIndex)
{
case 0:
lMethodName = "Sum";
break;
...
}
RunTest(lMethodName, (sender as Button).Name == "bRunMultipleTimes");
}
private void RunTest(String aTestName, Boolean aIsMultipleTest)
{
...
for (Int32 i = 1; i <= lThreadCount; i++)
{
BaseThreadState lThreadWithState = GetThreadState(aTestName);
lThreadWithState.Count = lRequestCount;
lThreadWithState.ThreadID = i;
Thread lThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(lThreadWithState.ThreadProc));
lThread.Priority = GetRandomThreadPriority();
lThread.Start();
}
}
private BaseThreadState GetThreadState(String aMethodName)
{
BaseThreadState lResult = null;
switch (aMethodName)
{
#region SumMethodThreadState
case "Sum":
SumMethodThreadState lSum = new SumMethodThreadState();
lSum.A = Convert.ToInt32(edSum1.Value);
lSum.B = Convert.ToInt32(edSum2.Value);
lResult = lSum;
break;
#endregion
...
}
}