Session Types sample (Delphi)
Overview
This example shows the essence of sessions and various session managers usage:
Prerequisites
Some parts of this sample require the following:
- Olympia Server to be running on the same computer with the sample server application
- MS SQL database server available on the same computer with the sample server application
- MS SQL server should have
Northwindsample database installed and a custom table created in this database:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Sessions] (
[SessionID] [char] (38) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[Created] [datetime] NULL , [LastAccessed] [datetime] NULL ,
[Data] [IMAGE] NULL )
Getting Started
- Build or compile all projects.
- Launch the server (via the menu option:
Tools -> Remoting SDK -> Launch Server Executable).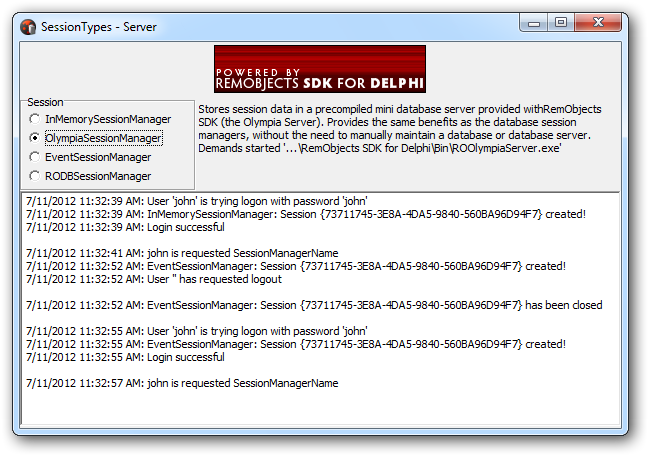
- Activate the session manager option desired.
- Make sure required servers are up and running.
- Launch the client.
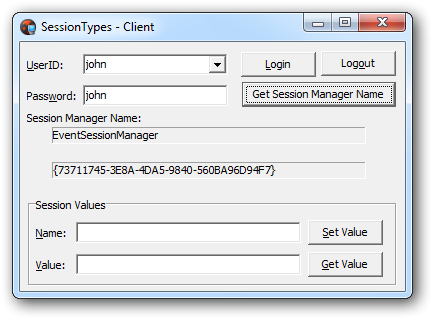
- Perform login with any
UserID,Passwordshould be equal to the login name. - See the
Session IDdisplayed after login. - Check the session manager by clicking the
Getbutton next to theManager Namefield. - Input
NameandValuethen clickSet Valuebutton. The value will be stored in the session. - Erase the content of the
Valuefield then clickGet Valuebutton. The value will be read from the session and displayed back to the field.
Examine the Code
- Session storage is not accessible from client directly so we use a couple of methods of the service to get and set values (
SessionTypesService_Impl.pasfile):
function TSessionTypesService.GetSessionValue(const Name: Unicodestring): Unicodestring;
begin
// ...
result := VarToStr(Session.Values[Name]);
// ...
end;
procedure TSessionTypesService.SetSessionValue(const Name: Unicodestring; const Value: Unicodestring);
begin
// ...
Session.Values[Name] := Value;
// ...
end;
- Examine the simple login service implementation (
LoginService_Impl.pasfile). Accessing theSessionproperty creates the session if it is not created yet, callingDestroySessiondestroys it. According to the protected services design guidelines theworkingservice requires session to be created when this service is called (RequreSessionproperty is set to true).
function TLoginService.Login(const UserID: Unicodestring; const Password: Unicodestring): boolean;
begin
// ...
result := (UserID <> '') and (UserID = Password); // Dummy test... You would code the one specific to your system
if Result then begin
Session.Values['Login'] := UserId;
Session.Values['Password'] := Password;
Log('Login successful');
end
else begin
Log('Invalid login!');
DestroySession; // Wrong login! The session cannot be persisted
end;
end;
procedure TLoginService.Logout(const SessionID: Unicodestring);
var
aUser: Unicodestring;
begin
if Session.Values['Login'] <> Null then
aUser := Session.Values['Login']
else
aUser := '';
Log('User ''' + aUser + ''' has requested logout');
Log('');
DestroySession; // Removes the session from the SessionManager
end;
- Event session manager introduces a set of events fired in response to operations performed with the session manager (creating, destroying, expiring sessions etc.). You could handle these events and implement any session storage you like, examine the following event handlers:
procedure TSessionTypes_ServerMainForm.EventSessionManagerReleaseSession(
var aSession: TROSession; NewSession: Boolean);
begin
// ...
end;
function TSessionTypes_ServerMainForm.EventSessionManagerGetSessionCount(
SessionManager: TROCustomSessionManager): Integer;
begin
result := EventSessionList.Count;
end;
procedure TSessionTypes_ServerMainForm.EventSessionManagerDeleteSession(
const aSessionID: TGUID; IsExpired: Boolean);
begin
// ...
end;
procedure TSessionTypes_ServerMainForm.EventSessionManagerClearSessions(
SessionManager: TROCustomSessionManager; OnlyExpired: Boolean);
begin
// ...
end;
procedure TSessionTypes_ServerMainForm.EventSessionManagerFindSession(
const aSessionID: TGUID; out aSession: TROSession);
begin
// ...
end;
Important note: this sample's custom session manager needs to create a session table in one of your databases. By default, the sample looks for the Sessions table in MSSQL's Northwind Database, but you can easily change to connect to another database by changing the connection string in CustomSessionManager.cs.
Data Abstract Users
This sample can easily be extended to encompass Data Abstract via the following steps:
- Create TDAConnectionManager, TDADriverManager, TDAADODriver and TDASchema instances.
- Relink.
- In the schema, create the datasets and commands similar to qu* (
TADOQuery). - Create a TDADBSessionManager instance and assign the corresponding datasets and commands.